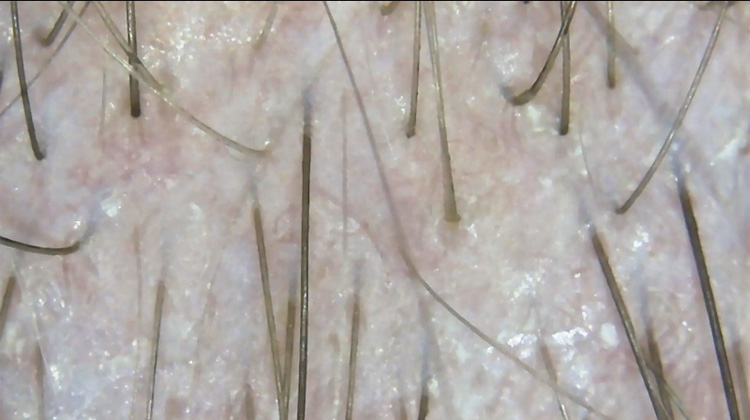
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stress. While it’s essential for regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure, excessive levels of cortisol can have detrimental effects on our health, including hair loss, disrupted sleep patterns, and stomach malabsorption.
Cortisol and Hair Loss:
1. **Hair Growth Cycle Disruption:** Cortisol can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle by pushing hair follicles into the telogen (resting) phase prematurely. This leads to increased shedding and thinning of the hair.
2. **Inflammation:** Elevated cortisol levels can trigger inflammation in the scalp, leading to conditions such as alopecia areata, where the immune system attacks hair follicles, resulting in hair loss.
3. **Reduced Nutrient Absorption:** Cortisol can impair the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals, which are crucial for healthy hair growth.
Cortisol and Sleep Deprivation:
1. **Disrupted Sleep Patterns:** Excess cortisol can interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and overall poor sleep quality.
2. **Increased Alertness:** High cortisol levels can keep the brain in a state of heightened alertness, making it difficult to relax and unwind, further exacerbating sleep issues.
3. **Impaired REM Sleep:** Cortisol can suppress REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is essential for cognitive function, memory consolidation, and overall well-being. Lack of REM sleep can contribute to daytime fatigue and cognitive impairment.
Cortisol and Stomach Malabsorption:
1. **Reduced Stomach Acid Production:** Excessive cortisol can suppress the production of stomach acid, impairing digestion and nutrient absorption. This can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, iron, and magnesium.
2. **Increased Gut Permeability:** Cortisol can contribute to increased gut permeability (leaky gut), allowing undigested food particles and toxins to enter the bloodstream. This can trigger inflammation and immune responses, further compromising nutrient absorption.
3. **Altered Gut Microbiota:** Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to dysbiosis and gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Managing Cortisol Levels:
1. **Stress Management Techniques:** Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and mindfulness can help lower cortisol levels and mitigate its negative effects on the body.
2. **Healthy Lifestyle Choices:** Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods, getting regular exercise, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and prioritizing self-care can support overall well-being and help regulate cortisol levels.
3. **Seeking Professional Help:**
If cortisol levels remain consistently elevated and are impacting daily functioning, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
They can provide personalized recommendations and interventions to address underlying stressors and restore hormonal balance.
In conclusion, cortisol plays a vital role in the body’s stress response, but when levels become chronically elevated, it can have profound effects on hair health, sleep patterns, and digestive function.
By implementing stress management strategies and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can mitigate the negative impact of cortisol and promote overall wellness.
Hormones play a significant role in regulating cortisol levels, and changes in hormone levels during perimenopause and menopause can contribute to cortisol fluctuations, creating a hormonal roller coaster effect. Here’s how hormones influence cortisol levels during these stages:
Perimenopause:
1. **Estrogen Decline:**
During perimenopause, estrogen levels begin to fluctuate and decline. Estrogen helps regulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls cortisol production. As estrogen levels drop, the HPA axis may become dysregulated, leading to irregular cortisol secretion patterns.
2. **Progesterone Fluctuations:
Progesterone, another hormone that declines during perimenopause, can also affect cortisol levels. Progesterone has calming effects on the nervous system and can help regulate cortisol production. Fluctuations in progesterone levels may contribute to cortisol imbalances and heightened stress responses.
3. **Stress Sensitivity:** Changes in hormone levels during perimenopause can make women more sensitive to stressors. Elevated cortisol levels in response to stress can further disrupt hormone balance, exacerbating symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances.
Menopause:
1. **Estrogen Deficiency:** Menopause marks the cessation of menstruation and a significant decline in estrogen production. Estrogen plays a role in modulating the stress response, and its deficiency can lead to dysregulation of the HPA axis and cortisol imbalances.
2. **Impact on Sleep:** Sleep disturbances are common during menopause, partly due to hormonal changes. Disrupted sleep patterns can contribute to alterations in cortisol secretion, as cortisol levels typically follow a diurnal rhythm that is influenced by the sleep-wake cycle.
3. **Vasomotor Symptoms:** Hot flashes and night sweats, common symptoms of menopause, can trigger stress responses and elevate cortisol levels. Chronic activation of the stress response system can lead to increased cortisol secretion and exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and irritability.
Managing Hormonal Roller Coaster During Perimenopause and Menopause:
1. **Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):** HRT can help alleviate symptoms of hormonal fluctuations by replenishing estrogen levels. However, it’s essential to discuss the risks and benefits of HRT with a healthcare provider, as it may not be suitable for everyone.
2. **Stress Management:** Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help modulate cortisol levels and mitigate the impact of stress on hormone balance.
3. **Healthy Lifestyle Habits:** Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, prioritizing sleep hygiene, and avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption can support hormone balance and overall well-being during perimenopause and menopause.
4. **Supplementation:** Certain supplements, such as adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha and rhodiola, may help support adrenal function and cortisol regulation. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements, especially during menopause.
By addressing hormonal imbalances and implementing lifestyle strategies to manage stress, women can navigate the hormonal roller coaster of perimenopause and menopause with greater ease and maintain their overall health and well-being.
Adjusting lifestyle holistically involves making changes that address various aspects of your well-being, including physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health. Here are some holistic lifestyle adjustments you can consider:
1. **Mindful Eating:** Focus on consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods and eating mindfully. Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, and choose foods that nourish your body and support optimal health.
2. **Regular Exercise:** Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiming for a mix of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Find activities you enjoy and make movement a natural part of your day.
3. **Quality Sleep:** Prioritize sleep hygiene by establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment for restorative rest. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night.
4. **Stress Management:** Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness. Engage in activities that promote relaxation and help you manage stress effectively.
5. **Social Connections:** Cultivate meaningful relationships and social connections with friends, family, and community members. Spend time with loved ones, engage in enjoyable social activities, and prioritize communication and connection.
6. **Emotional Well-being:** Take time to check in with your emotions, acknowledge and express them in healthy ways, and seek support when needed. Engage in activities that promote emotional resilience, such as journaling, therapy, and creative expression.
7. **Mind-Body Practices:** Explore mind-body practices such as yoga, tai chi, qigong, and acupuncture, which integrate physical movement with breath awareness and mindfulness to promote holistic well-being.
8. **Nature Connection:** Spend time in nature regularly, whether it’s going for walks in the park, hiking in the mountains, or simply spending time in your garden. Nature has a grounding and rejuvenating effect on the mind, body, and spirit.
9. **Personal Growth:** Engage in activities that promote personal growth and self-discovery, such as reading, learning new skills, setting goals, and pursuing hobbies and interests that bring you joy and fulfillment.
10. **Spiritual Nourishment:** Cultivate a sense of purpose, meaning, and connection to something greater than yourself. Explore spiritual practices and beliefs that resonate with you, whether it’s through prayer, meditation, contemplation, or participation in religious or spiritual communities.
By embracing these holistic lifestyle adjustments, you can support your overall well-being and cultivate a healthier, more balanced life. Remember that small, consistent changes over time can lead to significant improvements in your physical, mental, and emotional health.
Ibana Villasenor
Hair Holistic Eco-Salon
www.hairholistic.com

The best place in Morocco

Enjoying views of Lisbon